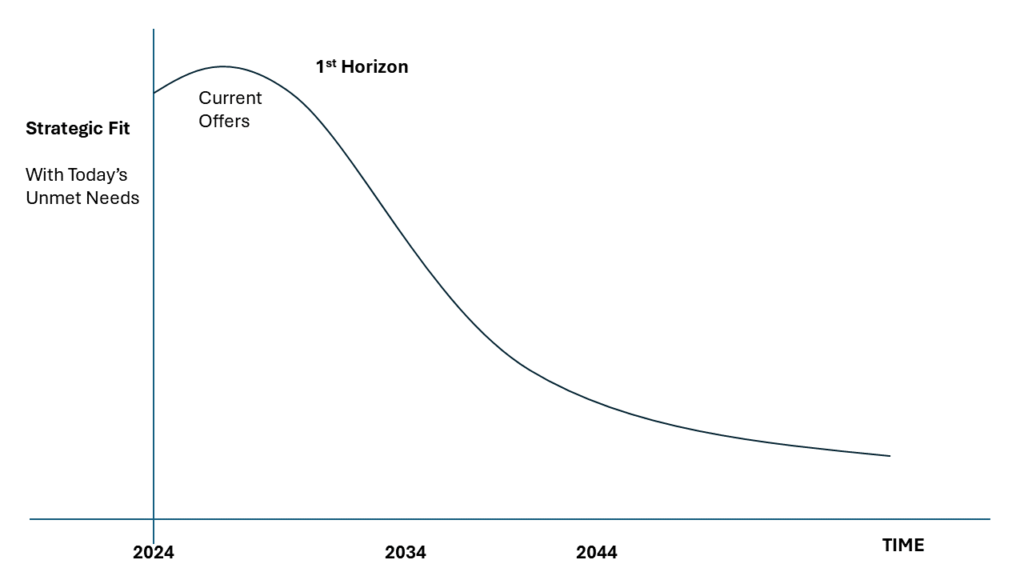
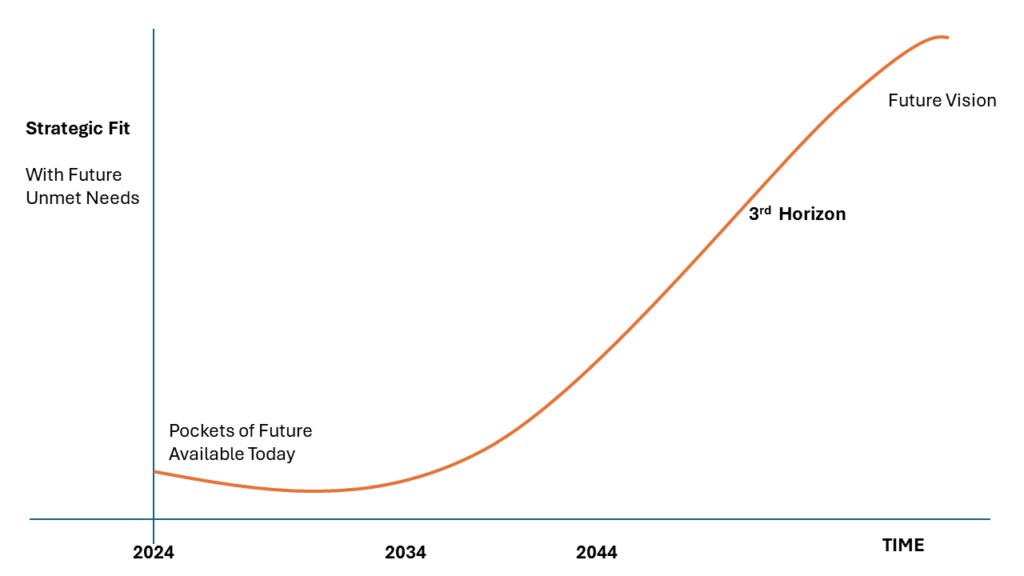
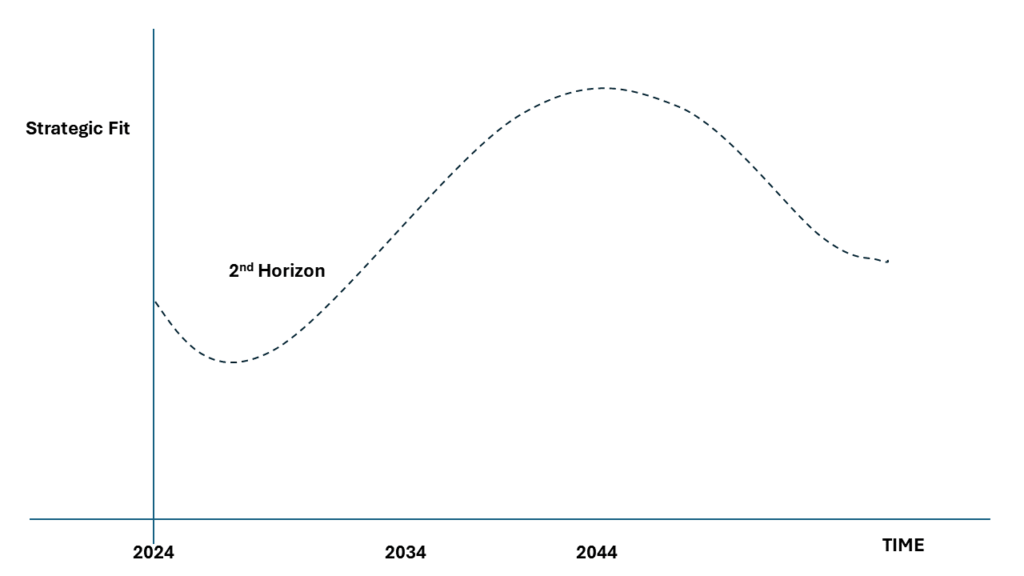
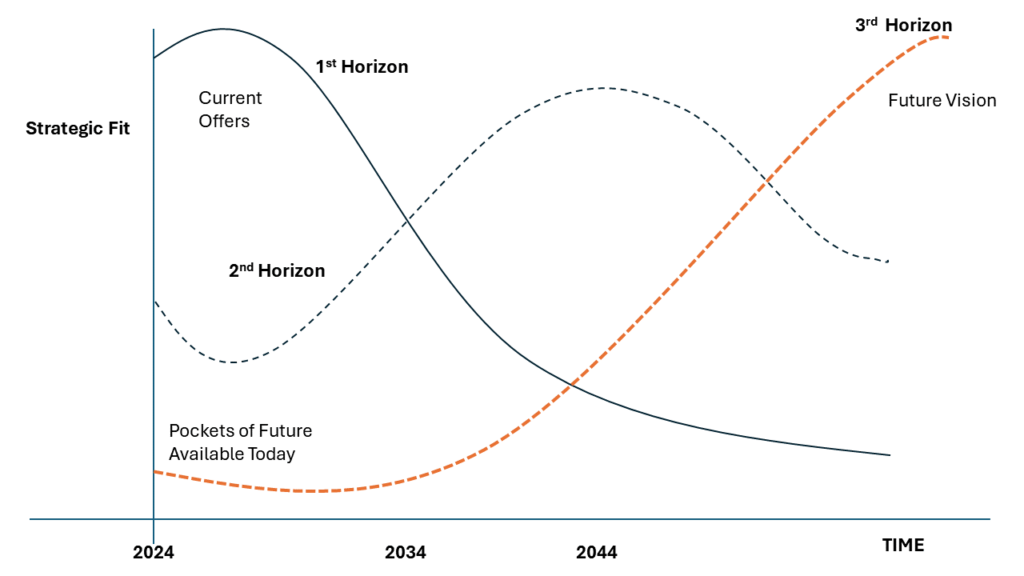




As a leader, you navigate a relentless sea of deadlines and short-term goals. The pressure to be agile and decisive is immense. Yet, amidst the daily chaos, a powerful tool often gets neglected – the long-term vision. You might believe it’s a luxurious indulgence, a distant dream with little bearing on the here and now. But what if I told you that fostering a vision for a faraway future can have a profound impact on your company’s immediate performance?
Beyond the Transaction: Unlocking Deep Inner Motivation
Think about the difference between extrinsic and intrinsic motivation. Many managers rely on the former – bonuses, commissions, and other forms of immediate rewards. These tactics can get results, but they fail to tap into the wellspring of human drive that lies beyond mere compensation.
Consider the most inspiring individuals you know. They may dedicate years to raising children, contribute to charity, or pursue long-term educational journeys. These actions highlight the power of delayed gratification, where the inherent value of the goal fuels sustained effort.
Unfortunately, most companies fall short of harnessing this power. When every task is framed as a transactional exchange – “I give you money, you give me work” – employees become conditioned to expect a tangible reward for every action. This transactional approach stifles intrinsic motivation, leaving them feeling uninspired and disengaged.
But imagine if you offered your team a chance to invest in their own futures, a future inextricably linked to the company’s success. Here, we’re not talking about vague pronouncements about “balanced sheets” or “customer benefits.” You need to co-create a compelling vision of the future, one that resonates with everyone on board.
Think about the GraceKennedy 2020 Vision and Vision 2030 Jamaica projects. These initiatives, crafted collaboratively with hundreds of people, charted a course spanning over two decades. Despite their extended timeframes, they demonstrably ignited immediate action.
In some companies, employees are so energized by their shared vision, they even volunteer to sell products on their own time. This illustrates the power of a long-term vision to motivate and inspire immediate action.
Navigating Storms with Purpose: Focus During Emergencies
In today’s volatile business landscape, agility and adaptability are crucial. You need a workforce that can respond swiftly to unforeseen challenges. However, relying solely on a reactive, adrenaline-fueled approach has its limitations. Chronic stress can lead to burnout, and a workplace solely focused on solving the immediate problem at hand lacks direction.
This is where a long-term vision steps in. It provides the necessary context that goes beyond simply “getting through the day” or “surviving the crisis.” It allows your employees to remain two-headed, addressing immediate challenges while keeping the long-term vision in sight.
Let’s use customer service as an example. Reactive customer service often prioritizes every single complaint, regardless of its validity. But a strategic vision, informed by a long-term perspective, can create a framework for prioritizing customers. Remember Michael Porter’s quote: “Strategy is about making choices, trade-offs; it’s about deliberately choosing to be different.”
When your employees understand the invented future, it shapes each customer interaction as a strategic choice, not just an obligation. They can use the vision to guide their decisions, prioritizing interactions that align with the company’s long-term goals.
These are just a few examples of how a long-term vision can positively impact your immediate performance. A forward-looking vision acts as a test of your leadership clarity – the ability to inspire action today by painting a compelling picture of tomorrow. When you plant the seeds of a distant future, you cultivate a more engaged, motivated, and strategically focused workforce that can weather any immediate storm and navigate towards a brighter shared future.
This revised version maintains the use of the second person (“you”) while offering a more professional and engaging tone. It emphasizes concrete actions you can take and highlights the practical results of fostering a long-term vision.
In the workplace, your employees can be remarkably sensitive. The slightest hint of bad news ignites a wildfire of rumors, fueled by the rapid spread of WhatsApp messages.
What you perceive as unproductive behavior is often the result of your interventions only addressing surface-level symptoms rather than the root causes. As soon as you tackle one popular complaint, another fresh grievance emerges to take its place, leaving you feeling like you’re trapped in a never-ending cycle.
To break free from this pattern, it’s essential to rethink your approach to addressing thin-skinned staff. Instead of merely treating the symptoms, consider these three strategies for fostering a more profound sense of purpose and inspiration among your employees.
Hurricane Heroics: Unleashing Extraordinary Potential
In the aftermath of a natural disaster, such as a hurricane, we often witness acts of everyday heroism. Neighbors who once refused to speak to one another put aside their differences and unite to overcome the shared challenge at hand. In the face of life-threatening disruptions, people tap into hidden reserves of resilience and compassion.
But what if this extraordinary energy and resolve could be harnessed within the workplace, without the need for a catastrophic event to occur?
The answer lies in understanding the powerful influence of the future on human behavior. When people have something significant to look forward to, they inherently act differently. The problem is that many employees have become jaded, expecting only disappointments and discomforts from the future. This negative mindset fuels their hypersensitivity, causing them to perceive every error as a personal slight.
However, what if this obsession with the future could be reframed as an opportunity rather than a hindrance? Perhaps their reactions stem from a genuine desire to care about the future, and there’s a way to channel this passion in a more constructive direction.
An Urgent, Inspiring Future: Harnessing the Power of Purpose
The ability to envision a return to normalcy is what empowers people to bounce back swiftly after a hurricane. This imagined future provides them with something to look forward to, uplifting and inspiring them even in the face of tremendous loss.
As they survey the wreckage, they help others find hope, moving themselves out of their comfort zones, taking risks, overcoming historical biases, forgiving debtors, sacrificing time, and donating money. In other words, they tap into their hidden reserves of discretionary resources to spend untapped treasure.
As an employer, witnessing this transformation in the same staff members who nearly went on strike over cafeteria lunches can be astonishing. However, instead of dismissing your people as unsolvable mysteries, it’s crucial to recognize their wider humanity. As Friedrich Nietzsche said, “Those who have a ‘why’ to live, can bear with almost any ‘how’.”
Offering your staff a compelling “why” can be achieved by crafting a joint future that deviates from the default trajectory.
Your Company’s Peculiar Destination: Embracing Discomfort for a Greater Purpose
Most employees go through the motions, primarily concerned with their creature comforts and conveniences rather than anything else. In response, many managers become afraid to ask too much, habitually lowering their expectations to avoid conflict.
However, the reality is that they simply aren’t asking for enough.
Imagine a manager who asks their staff, “Are you OK?” each day. Eventually, someone musters the courage to respond, “No, I’m not.” The manager inquires about the issue, resolves the problem, but continues to ask the same question the next day, perpetuating a cycle of addressing surface-level concerns.
Now, consider a dramatic alternative: A manager convenes their staff to create a vivid picture of the department’s future – an invented future that goes well beyond business-as-usual. This joint aspiration becomes a win-win for all involved, instantly repelling those who are the most resistant while attracting the best employees who crave a greater sense of purpose.
It’s as if a metaphorical hurricane has swept through, igniting a shared desire to take extraordinary actions, even if they cause personal “discomfort.” This phenomenon was observed by Holocaust survivor Viktor Frankl, who noted that those who found a “why” were more likely to survive the concentration camps. Additionally, Frankl stated:
“… mental health is based on a certain degree of tension, the tension between what one has already achieved and what one still ought to accomplish… Such a tension is inherent in the human being…”
“We should not, then, be hesitant about challenging man with a potential meaning for him to fulfill…What man actually needs is not a tensionless state but rather the striving and struggling for a worthwhile goal, a freely chosen task. What he needs is not the discharge of tension at any cost but the call of a potential meaning waiting to be fulfilled by him.”
Unfortunately, prioritizing purpose over comfort is a concept rarely taught in classrooms. However, it offers managers a powerful tool to inspire and engage their employees. By crafting a shared vision of a future that transcends the mundane, you can tap into your staff’s innate desire for meaning, fostering a sense of urgency and determination that propels them beyond their perceived limitations.
In the face of adversity, people are capable of remarkable feats. As a leader, your role is to create an inspiring “why” that ignites the same level of passion and commitment, transforming insults and hypersensitivity into a relentless pursuit of a greater purpose.
You are a leader, and are well aware that both private and public sector organizations must prioritize long-term thinking. As a result, you can immediately enumerate some of the main reasons.
However, there are persistent corporate issues that appear unrelated to long-term planning. Therefore, their sudden presence catches leaders off-guard. Failing to complete a long-term strategic plan can lead to three anticipated but uncommon issues.
1. Commitments at Cross-Purposes
Consider an organization that has invested substantial time and effort into crafting a meticulous three-year strategic plan. The document lays out clear goals, milestones, and performance indicators to work towards over that relatively short timeframe. However, when gazing further into the future, a lack of cohesion emerges among the executive team and board members. Each leader has their own personal vision for where the company should be in four, ten, or thirty years. But there is no consensus or shared strategic roadmap beyond the three-year horizon.
This divergence in perspectives can undermine decision-making processes. Without alignment on long-term direction, executives rely on their own criteria when charting the future course. The cumulative impact of this disjointed approach to leadership can be highly detrimental. It leads to missed opportunities, strategic missteps, and organizational stagnation or decline. Unified commitment to a long-term vision enables more focused decision-making and progress.
In addition to this problem, there is also a detrimental effect on the top issue that organizations often report in their strategic planning – the lackluster execution. In the absence of a long-term vision, perceptive executives often find themselves involuntarily holding back their support. Why?
They can tell that the commitment is superficial. And likely to shift in a moment. Hence, it is unnecessary to invest precious social capital, budget, and time into a fleeting plan that may have a 50% likelihood of being discarded.
I recently revisited Competing for the Future by Hamel and Prahalad, immersing myself once again in their groundbreaking insights. In this 1994 classic, they accurately foresaw the influence of emerging technologies.
It was quite interesting to note that they were mostly correct in their observations. Taking their predictions seriously would have allowed a company to establish a distinct competitive edge.
However, this is only one small section of the larger landscape. You may be familiar with the comprehensive PESTEL suite, which encompasses Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal/Regulatory factors. By only planning with a short-term horizon, companies fail to acknowledge the cumulative effects of gradual trends in all these areas simultaneously.
By doing so, they make themselves vulnerable to potential dangers. Additionally, they miss out on significant opportunities because they fail to consider the hidden possibilities.
For example, Apple had a visionary glimpse into the future, imagining a comprehensive ecosystem that revolved around their products, services, and the cloud. Most likely, they were in possession of the identical information as everyone else. What set it apart?
Around 2010, they devised a comprehensive plan that spanned a decade, gradually constructing a complete solution, piece by piece. From their near-collapse in 1997, they have risen to become one of the most valuable companies in the world today. In the face of an existential threat, they boldly seized an opportunity that came their way.
Most organizations find it challenging to create succession plans. Why? Letting incumbents go unchallenged and accepting their perpetual rule is the easier option.
It’s only when you consider the long-term consequences that you realize the folly of this approach.
For example, it becomes evident that the necessary skills to navigate the company through upcoming transitions are lacking. A person nearing retirement may not be the most suitable candidate for tackling a new learning curve.
But that’s just scratching the surface. As soon as talented middle managers sense the lack of long-term direction, the sights of them browsing job listings and attending networking events become more frequent.
Over time, companies find themselves staffed by an ineffective majority, trapped in a state of stagnation. However, the situation takes a turn for the worse. Eventually, as the “last men standing”, members of this cohort receive promotions, even to the highest executive positions.
To prevent these three slow-moving disasters, your team must engage in strategic planning that integrates short and long-term perspectives.
You are someone who is already a long-term thinker, working in a for-profit company. Unlike many, you don’t need to be convinced about the importance of long-term thinking. Somewhere early in the past – childhood, early career – you embedded the idea in your thinking. Now balancing short and long term thinking is a part of your character.
But this may be why you are confused. Others around you don’t share this trait. In fact, you feel like a fish out of water – always harping on the need for long-term thinking, sometimes asking inconvenient questions.
You can’t understand why others don’t share your concern. And it’s not that you are particularly ESG, sustainable or anything like. Nor do you come from an old-school. You sense that the company would make better decisions if it had more than the usual 3-5 year plan.
But how do you convince others in the C-Suite, and the board, to think with an additional lens?
Tune into this episode as I tackle this wicked problem.

Similar to most organizations, your company also has a vision or purpose statement. The initial idea was meant to ignite inspiration, but lately, it seems to have lost its allure. What interventions can you implement to foster a collaborative environment and encourage your staff to go above and beyond? And how does this statement support the goals outlined in your corporate strategy?
It is easy to comprehend the reasons for creating a compelling vision.
As we human beings look to the future, our imaginations run wild with the anticipation of what lies ahead, just beyond the corner. As such, while sitting at work on a Friday afternoon, we’re happy, feeling the anticipation of the weekend ahead.
By mid-day on Sunday, our energy levels plummet and a sense of unease settles in. Why? Monday looms ahead, and with it comes the familiar routine and the anticipation of the weekly grind.
Our psychology is wired to have an addictive tendency to anticipate what lies ahead. Sadly, this fact goes unnoticed by most individuals. The lack of understanding about the future, even among progressive companies, is the reason why social media has such a powerful draw for the average employee.
A company vision is management’s way of providing an alternative, and they offer five options to choose from.
1. **The Invisible Vision**: This form of vision exists solely within the mind of the company’s top leadership. While these individuals may be passionate about their vision, they fail to share it with the rest of the organization. Communication barriers or a desire to maintain control often lead to this secretive approach. As a result, employees are left in the dark, lacking a sense of direction and purpose.
In this first category, if no one besides the top leader knows where your organization is headed, it may be the case.
2. **The Vague Vision**: Perhaps the most common form, vague visions lack clarity and specificity. These statements are often found adorning office walls or buried within corporate documents. While they may sound lofty and inspirational, they fail to provide actionable guidance. Without clear goals and timelines, employees struggle to connect their daily tasks to the overarching vision, resulting in disengagement and apathy.
To determine if your company’s statement is vague, try this simple test. Reflect on whether a rational employee could perceive that the objective has already been fulfilled or is on the verge of completion. Is it done?
Additionally, is there a specific year associated with it? If the answers are simply “Yes” and “No”, it can be considered too vague, leaving room for people to only pay it lip-service.
Honestly…it would be more accurate to call it a slogan.
3. **The Squeezed-Up Vision**: In an attempt to avoid ambiguity, some organizations opt for short-term visions. However, these compressed timelines often lead to unrealistic expectations and limited scope. Employees may feel overwhelmed by the pressure to achieve short-term goals without a broader long-term perspective. As a result, motivation wanes, and morale suffers as employees become disillusioned with unattainable targets.
4. **The Strategy-Less Vision**: Even with clearly defined goals, a vision can falter without the support of a comprehensive strategic plan. In this scenario, organizations set ambitious targets but fail to provide a roadmap for achieving them. Without alignment between the vision and strategic objectives, employees are left to navigate uncertain terrain on their own. As a result, initiatives lack direction, resources are mis-allocated, and progress stalls.
But above all, they realize the groundwork has not been done because it fails to confront reality. As such, they believe the vision won’t be implemented.
On the flip side, there is:
**The Ideal Vision**: This represents the pinnacle of corporate visioning, combining clarity, inspiration, alignment, and engagement. An ideal vision is clear and concise, providing a roadmap for the organization’s future. It inspires passion and commitment among employees, fostering a sense of purpose and belonging. Moreover, it is aligned with the organization’s strategic objectives, ensuring that every action moves the company closer to its goals. Finally, it engages employees at all levels, soliciting their input and fostering a culture of collaboration and innovation.
In conclusion, the strength of a corporate vision lies in its ability to provide clear direction, inspire action, and drive meaningful progress. By understanding the various forms of corporate visions and striving for the ideal, organizations can chart a course for success in today’s dynamic business environment.
This is a free preview of a paid episode. To hear more, visit longtermstrategy.substack.com
You are attending a strategic planning offsite and notice that the room has been quiet. Apart from the usual contributions from the CEO and experienced members of the C-Suite, the others are silent.
When they do speak up, it seems as if they are in a regular department meeting, addressing daily concerns. They aren’t thinking strategically.
You want to intervene, but don’t know where to begin.
Tune into this episode to hear from me and my special guest, Svyatoslav Biryulin, as we tackle this wicked problem together.
Show Notes
The full video of the discussion is available for paid members. See below.
Svyatoslav Biryulin is a strategy consultant. Before founding his own consulting boutique, Svyatoslav worked for over 20 years in various commercial enterprises, of which 13 years in a CEO position. Since 2012, he has been serving on the boards of directors of companies in various countries, leading strategy committees. He is an active blogger and publicist and lives in Ljubljana, Slovenia https://www.linkedin.com/in/biryulin/
https://svyatoslav.substack.com
View the full video discussion as a paid member, or with a trial membership.